Chandrayaan-3: Lunar Crater Detected; First Readings of Moon Surface Temperature
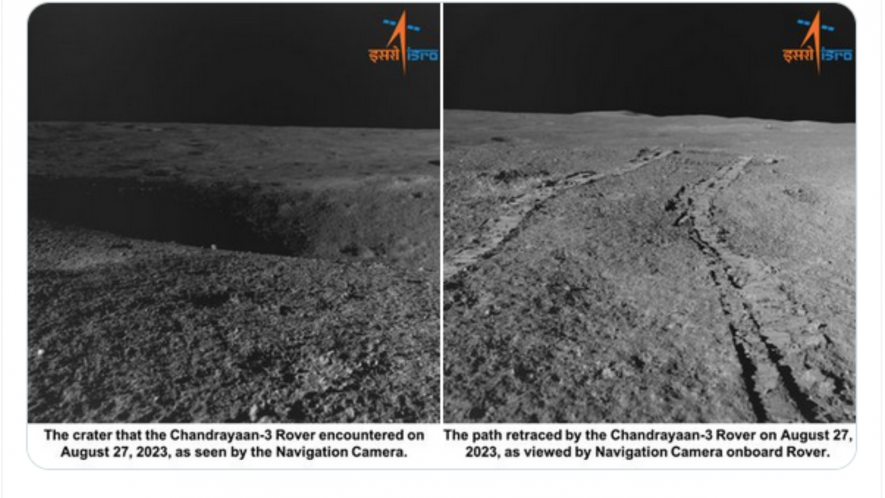

The latest image released by ISRO of the 4-meter crater encountered by Pragyan. Source: ISRO
After landing successfully on the Lunar South Pole, the Chandrayan-3 lander Vikram has reported to have sent the first readings about the moon surface. As the ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) said on August 27,in its X (Twitter) handle, the Vikram lander has sent the temperature profile of the lunar topsoil around the pole. The ChaSTE (Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment) payload recorded the temperature profile of the surface.
According to ISRO, the payload (payload is a scientific or technological instrument on board the craft designed to carry specific tasks) can penetrate to a depth of 10 centimetres beneath the lunar surface in a controlled manner. This is fitted with 10 individual temperature sensors.
The temperature record graph as ISRO published is as follows
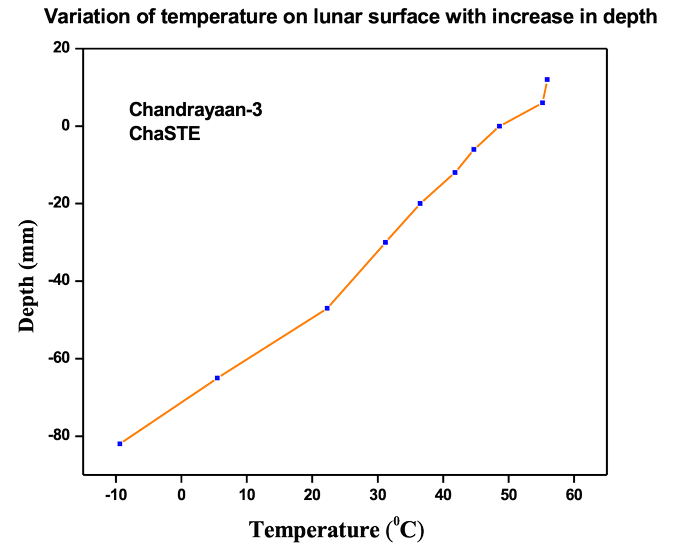
Source: ISRO.
The graph is a projection of the variation in temperature of the lunar surface at various depths. This temperature profile came out from the ChaSTE recording during its penetration.
The graph tells that at a depth of 8 centimetres, the temperature of the lunar surface as minus 10 degree Celsius and it steadily rises when the probe (the instruments) came to the surface and at a height of around 10 centimetres above the surface the temperature recorded was 55 degree Celsius. The graph depicts that the lunar surface temperature is very sensitive with respect to its depth.
ISRO says that the presented graph is an illustration of the temperature variations of the “lunar surface/near-surface at various depths, as recorded during the probe's penetration. This is the first such profile for the lunar south pole.” The agency also says that detailed observations are underway.
ISRO also has reported detecting a four-meter lunar crater by the rover Pragyan, which was situated 3 meters ahead of the rover’s position. The rover is now safely heading on a new path, ISRO said.
Lunar craters are the circular shapes or cavity in its surface. The lunar surface is full of such craters formed when rocks or comets from the space hit the surface. As these craters are formed from such impacts, these are called the impact craters.
The Lander and the Rover Payloads
As ISRO says, the Chandrayan-3 mission is a “follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface.” The mission has lander and rover modules. The lander module is designed for safe landing on the moon surface, while the rover is aimed to roam over it to collect various information the Chandrayan-3 mission aims to achieve.
For this purpose, both the lander and the rover are equipped with a variety of payloads or instruments on board. The mission has the objective of conducting in-situ (at the original place) along with demonstrating safe and soft landing on lunar surface and movement of the rover.
Lander Payloads
The lander Vikram has four payloads, namely, the ChaSTE, RAMBHA (Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive ionosphere and Atmosphere), ILSA (Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity) and the LRA (LASER Retroreflector Array).
The ChaSTE is designed to carry out the thermal measurements of the lunar surface near the polar region, where it landed, while the RAMBHA is sent with an aim of measuring the near surface plasma (ions and electrons) density and how it changes over time.
The ILSA aims to detect the seismicity around the site where Vikram landed and outlining the lunar crust and mantle structure and the LRA, a passive laser reflector array provided by NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration), the US aims for studying the dynamics of the Moon system.
The rover module of Chandrayan-3, the Pragya rolled out of the lander after a day of the soft-landing. The rover is aimed to carry out chemical analysis in-situ about the lunar surface. The rover will move to the highlands of Moon’s south pole.
Pragyan, the six-wheeled rover will carry on experiments for 14 Earth days after landing, which is equivalent to one lunar day.
For the in-situ analyses, the rover is equipped with two payloads, namely the LIBS (LASER Induced Breakdown Spectroscope) and the APXS (Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer).
The LIBS has an objective of deciphering the mineralogical composition of the lunar surface. This payload will conduct quantitative and qualitative elemental analysis in order to understand the chemical composition of the lunar surface.
The APXS payload will specifically determine the elemental composition of Magnesium (Mg), Aluminium (Al), Silicon (Si), Potassium (K), Calcium (Ca), Titanium (Ti) and iron (Fe).
As rover Pragyan moves along its path in the lunar South pole, it is expected to continue sending further information about the lunar surface through the in-situ experiments during its lifetime of one lunar day.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.














