Ancient Human Genomes Shed New Light on Interbreeding of Humans and Neanderthals
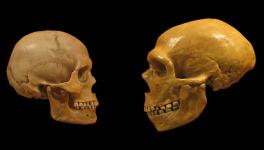
Today, the only living human species on Earth is the Homo Sapiens or the modern humans. The ancient times were different though; there were other human species as well, the important ones being the Neanderthals and the Denisovans. These two ancient human species are no more on the planet, but their signatures are still alive within us--the modern humans--who carry genes from these early humans in their DNA. This has been possible because our ancestors carried out interbreeding with those extinct early humans.
The interbreeding is a well-known fact and as a result of it, all non-African Human populations have Neanderthal genes that account for up to 2% of their DNA. Again, people from Melanesian, Aboriginal Australian and Papuan descent have even higher amount of Denisovan genes in their DNA.
Recently, two new genetic studies have come out with new findings about the extent of interbreeding of Homo Sapiens with the Neanderthals. The pair of studies went deeper into when the interbreeding happened and up to what extent.
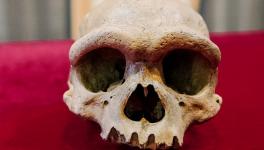
One study examined the skull of a woman found in Czech Republic and the other analysed the remains of three individuals found in Bacho Kiro cave in Bulgaria. The analyses showed that the age of all the specimens have been around 45,000 years. The woman whose skull was analysed is nicknamed as Zlatý kůň. The analyses also showed that all the specimens have substantial amount of Neanderthal genes and the interbreeding had happened relatively recently.
When modern humans interbred with Neanderthals, the immediate offspring has highest levels of Neanderthal DNA and also, this segment is longer. However, going down more generations, the DNA segments become shorter; this is because more of the Neanderthal DNA is not being added to the human DNA. Taking this into account, scientists could estimate about how far back the mixing of the DNAs could have taken place.
Mateja Hajdinjak, the lead author of the research about the Bacho Kiro cave in Bulgaria, commented, “We found that the Bacho Kiro Cave individuals had higher levels of Neanderthal ancestry than nearly all other early humans. Crucially, most of this Neanderthal DNA comes in extremely long stretches. This shows that these individuals had Neanderthal ancestors some five to seven generations back in their family trees.”
The research paper on the remnants excavated from Bacho Kiro cave was published in Nature on April 7.
Again analysis on Zlatý kůň showed that the woman had been removed from her Neanderthal ancestry just about 2,000 years ago. Yes, a span of 2,000 years is not that long a period compared to the human history. The researchers also claimed that Zlatý kůň represents the oldest known modern human genome that has been found so far.
The research about Zlatý kůň is published in Nature Ecology and Evolution and that too on April 7.
The scientists also delved into the descendants of these ancient people. Interestingly, it was found that none of them has genetically contributed to the local European populations. The remnants excavated from the Bacho-Kiro cave were found to be more close to populations of present day East Asia and Americas compared to the Europeans.
Zlatý kůň, similarly, has been found not to have any genetic continuity with modern human populations in Europe after about 40,000 years ago.
The studies not only showed that the interbreeding of Homo Sapiens with Neanderthals took place to a larger extent than it was thought earlier, but also they have provided an understanding about early human migrations to Europe.
Get the latest reports & analysis with people's perspective on Protests, movements & deep analytical videos, discussions of the current affairs in your Telegram app. Subscribe to NewsClick's Telegram channel & get Real-Time updates on stories, as they get published on our website.